Eye-The human eye, Contents
Eye
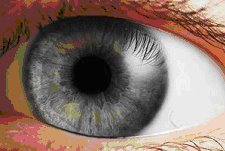
The human eye.
An eye is an organ of vision that detects light. Different kinds of light-sensitive organs are found in a variety of organisms. The simplest eyes do nothing but detect whether the surroundings are light or dark, while more complex eyes can distinguish shapes and colors. Many animals, including some mammals, birds, reptiles and fish, have two eyes which may be placed on the same plane to be interpreted as a single three-dimensional "image" (binocular vision), as in humans; or on different planes producing two separate "images" (monocular vision), such as in rabbits and chameleons.
============================
Contents
1 Varieties of eyes
2 Evolution of eyes
3 Anatomy of the mammalian eye
3.1 Three layers
3.2 Anterior and posterior segments
3.2.1 Anterior segment
3.2.2 Posterior segment
3.2.3 Other articles regarding eye anatomy
4 Cytology
5 Acuity
6 Dynamic range
7 Adnexa and related parts
7.1 The orbit
7.2 Eyebrows
7.3 Eyelids
7.4 Eyelashes
8 Eye movement
8.1 How we see an object
8.2 Color vision
8.3 Extraocular muscles
8.4 Rapid eye movement
8.5 Saccades
8.6 Microsaccades
8.7 Vestibulo-ocular reflex
8.8 Smooth pursuit movement
8.9 Optokinetic reflex
8.10 Vergence movement
8.11 Accommodation
9 Diseases, disorders, and age-related changes
10 External links
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Want fun then why wait? Click on any one of URLhttp://blog4people.coz.in/ http://jokes4children.coz.in/ http://adsense.coz.in/ http://kannada.coz.in/ http://ourmysore.coz.in/ http://wowbangalore.coz.in/ http://wowchennai.coz.in/ http://bhshistory.coz.in/ http://karaga.coz.in

The human eye.
An eye is an organ of vision that detects light. Different kinds of light-sensitive organs are found in a variety of organisms. The simplest eyes do nothing but detect whether the surroundings are light or dark, while more complex eyes can distinguish shapes and colors. Many animals, including some mammals, birds, reptiles and fish, have two eyes which may be placed on the same plane to be interpreted as a single three-dimensional "image" (binocular vision), as in humans; or on different planes producing two separate "images" (monocular vision), such as in rabbits and chameleons.
============================
Contents
1 Varieties of eyes
2 Evolution of eyes
3 Anatomy of the mammalian eye
3.1 Three layers
3.2 Anterior and posterior segments
3.2.1 Anterior segment
3.2.2 Posterior segment
3.2.3 Other articles regarding eye anatomy
4 Cytology
5 Acuity
6 Dynamic range
7 Adnexa and related parts
7.1 The orbit
7.2 Eyebrows
7.3 Eyelids
7.4 Eyelashes
8 Eye movement
8.1 How we see an object
8.2 Color vision
8.3 Extraocular muscles
8.4 Rapid eye movement
8.5 Saccades
8.6 Microsaccades
8.7 Vestibulo-ocular reflex
8.8 Smooth pursuit movement
8.9 Optokinetic reflex
8.10 Vergence movement
8.11 Accommodation
9 Diseases, disorders, and age-related changes
10 External links
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Want fun then why wait? Click on any one of URLhttp://blog4people.coz.in/ http://jokes4children.coz.in/ http://adsense.coz.in/ http://kannada.coz.in/ http://ourmysore.coz.in/ http://wowbangalore.coz.in/ http://wowchennai.coz.in/ http://bhshistory.coz.in/ http://karaga.coz.in
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Note :- All the information are given as per the news read by us, we are not responsible for any problem occured after reading this information. The contains of this blog is just for reference, for more information you can refer the books written by famous authors. The contains of this blog you can use for your own purposes not to reproduce or reprint.
Note :- All the information are given as per the news read by us, we are not responsible for any problem occured after reading this information. The contains of this blog is just for reference, for more information you can refer the books written by famous authors. The contains of this blog you can use for your own purposes not to reproduce or reprint.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home